With a focus on promoting participation, CPAdvance™ for speech pathologists provides critical training on the principles and specific interventions that are best supported by evidence for very young children with, or at risk of, cerebral palsy or similiar neuro-disabilities.
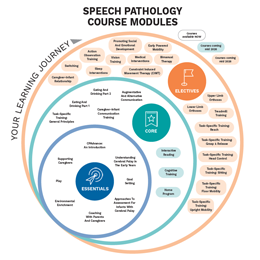
Click here to view your learning journey, what’s available now and what’s coming in 2026.
Course options include:
In the first release (available now) you can choose from three purchasing options: Essentials, Core or a bundle of Essentials and Core. You will receive credit for all courses completed.
Once the remaining Elective modules and the final assessment are released in mid-2026 and completed, you’ll earn your CPAdvance™ Accredited Practitioner certification.
Essentials - Course content
Cerebral palsy is the most common motor disability in childhood – yet every child is unique.
Today, we have powerful knowledge showing that diagnosing and intervening earlier can change life outcomes in profound ways for children with or at risk of cerebral palsy and their families. This introductory module establishes the three best practice key principles of early intervention that underpin each module of CPAdvance™.
By laying these foundations, this module offers learners a lens through which they can best engage with the knowledge and skill development offered throughout this program of learning, supporting real-life practice changes.
What is cerebral palsy? What causes it? How is it diagnosed?
This module aims to equip learners with foundational knowledge relating to cerebral palsy, with a particular focus on how it presents in the early years.
By completing this module, learners will gain an understanding of cerebral palsy diagnostic pathways, types, typographies and prognostic trajectories, as well as common comorbidities.
By deepening knowledge of cerebral palsy, learners will strengthen their ability to support caregivers in tailoring the most beneficial interventions for their goals and facilitating truly impactful therapy.
Goal setting with children and their families is a well recognised building block for effective practice. Yet, research shows that goal setting is often overlooked. Why do goal setting practices often fall short?
This module introduces the Rehabilitation Evidence-Based Decision Making (READ) model – a step-by-step layered process to setting goals with families.
Learners will understand how to collaboratively elicit and establish goals, transforming conversations with caregivers into caregiver-led plans that reflect evidence-based interventions that drive meaningful progress.
With the various assessments available, each with a different purpose, it is easy to feel uncertain as to which assessments should be prioritised and why. Sharing assessment feedback with families can also be complex and challenging.
This module aims to upskill learners in the assessment phase of care. Through this module, learners will be able to identify best available assessments for infants with or at risk of cerebral palsy, and apply assessment information to guide evidence-based intervention selection.
This module also aims to equip learners with assessment feedback skills using the SPIKES framework, promoting family engagement and therapeutic outcomes.
Coaching is an evidence-based approach in paediatric rehabilitation, that focuses on empowering families to unlock their child’s potential.
This module will introduce learners to the principles of coaching – what it is and how to do it with families to enable collaborative problem-solving so that they may enjoy the benefits of being informed decision makers in achieving their goals.
Our everyday environment is filled with opportunities for growth and learning. But how effectively do we intentionally leverage this potential to make therapeutic gains?
This module supports learners to understand how to optimise a child’s environment to stimulate social, cognitive, motor and sensory growth.
By understanding the evidence and theory of environmental enrichment, learners will develop the knowledge and skills required to support families to enhance their infant’s environment through paediatric rehabilitation service provision.
It is well known that ‘play’ is the most important job a child will ever have. But how well do we optimise play opportunities to achieve therapeutic goals?
This module supports learners to identify strategies to integrate play into therapy interventions by developing an applied understanding of the key ingredients of play that maximises an infant’s enjoyment, motivation and skill building.
Children learn more when they are having fun – making play essential for therapy intervention effectiveness.
Research consistently shows that caregiver well-being is linked to infant development. Yet, research also tells us that caregivers of children with disability are more likely to develop mental health and wellbeing challenges.
As the effectiveness of parent-led interventions and family centred practice is increasingly recognised, the need to support caregiver wellbeing and mental health in paediatric services is also emphasised.
This module aims to equip learners with principles and strategies to embed supporting caregiver mental health and wellbeing as part of routine practice. Caregiver well-being drives infant outcomes.
Early release Core - Course content
Cerebral palsy is the most common motor disability in childhood – yet every child is unique.
Today, we have powerful knowledge showing that diagnosing and intervening earlier can change life outcomes in profound ways for children with or at risk of cerebral palsy and their families. This introductory module establishes the three best practice key principles of early intervention that underpin each module of CPAdvance™.
By laying these foundations, this module offers learners a lens through which they can best engage with the knowledge and skill development offered throughout this program of learning, supporting real-life practice changes.
All children with cerebral palsy have some level of impairment in their motor development.
Early intervention emphasises the importance of practising specifically what the infant and the family want to learn, rather than general milestone-based programs.
Task-Specific Training is a powerful approach grounded in neuroplasticity and motor learning principles designed to develop skills in specific functional tasks.
This opening module aims to help learners understand the neuroscience evidence-base related to task-specific training and outline the principles of this approach for application in clinical practice.
Mealtimes are more than just food and drink – they are moments of connection, culture and shared ritual for families and community.
Children with cerebral palsy often experience challenges with eating and drinking, having significant nutritional and social implications.
As the primary role of a caregiver is to nourish their baby, it can be very distressing when eating and drinking is challenging.
This module, the first in in a two-part series, aims to equip learners with the knowledge and skills required to support infants with or at risk of cerebral palsy to develop eating and drinking skills, with a particular focus on managing fluids.
The balancing of skill development and safety can be complex for therapists, particularly in developing eating and drinking skills with infants who have or are at risk of cerebral palsy where there is a higher risk of oropharyngeal dysphagia.
This module is the second in a two-part series that aims to equip learners with the knowledge and skills required to work with these infants in developing eating and drinking skills.
This module focuses on managing oral intake of solids.
Communication is essential – it allows the expression of need and identity, connection with loved ones, and full participation in life.
However, most children with cerebral palsy experience difficulties with communication.
This module aims to upskill learners in the principles of communication development.
Complemented by coaching and a family centred approach, through this module learners will be able to apply evidence-based principles and communication strategies to identify appropriate communication goals, assessments and interventions at the just right level of challenge to progress communication skills of infants with or at risk of cerebral palsy.
Approximately 25% of children with cerebral palsy are unable to produce functional speech. AAC can support breaking barriers to communication – though this can often feel complex.
Challenging factors can include resources, family uncertainty, or simply not knowing where to start due to the range of systems and devices available.
This module aims to support therapists to understand the purpose, benefits of AAC – when and how to use specific AAC approaches across a range of diverse clinical scenarios to support the advancement of life-long communication skills in children with or at risk of cerebral palsy.
Have a question or query? Click here
We’d love to help you.